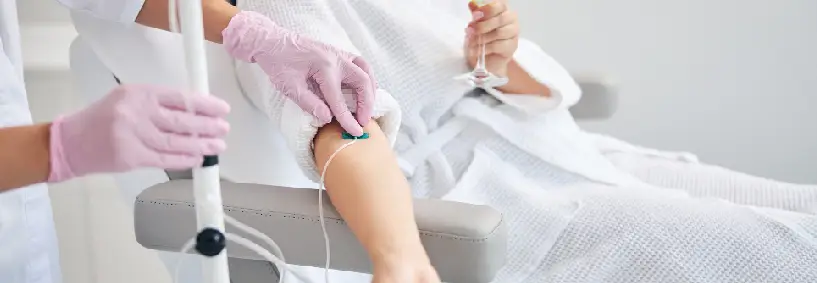
Alternative Treatments For Heart Disease
Q. What are some alternative treatments for heart disease?
A. Alternative treatments for heart disease include lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, stress management), supplements (omega-3 fatty acids, CoQ10), and therapies like acupuncture, meditation, and chelation therapy. These methods aim to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Benefits of Chelation Therapy
Q. What are the benefits of chelation therapy?
A. Chelation therapy is used to remove heavy metals from the body, which can help improve symptoms of heavy metal poisoning, cardiovascular disease, and other conditions. It may also enhance blood flow, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health.
Cardiovascular Chelation Therapy
Q. What is cardiovascular chelation therapy?
A. Cardiovascular chelation therapy involves using chelating agents to remove calcium deposits and heavy metals from the bloodstream, potentially improving blood flow and reducing the risk of heart disease.
Certified Chelation Therapist
Q. What is a certified chelation therapist?
A. A certified chelation therapist is a healthcare professional who has undergone specialized training and certification to administer chelation therapy safely and effectively.
Chelation Therapy
Q. What is chelation therapy?
A. Chelation therapy is a medical procedure that involves the administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals and other toxins from the body.
Chelation Therapy Clinics
Q. What are chelation therapy clinics?
A. Chelation therapy clinics are specialized medical facilities where patients can receive chelation therapy administered by trained professionals.
Chelation Therapy Doctors
Q. Who are chelation therapy doctors?
A. Chelation therapy doctors are medical professionals trained and certified to administer chelation therapy. They often have backgrounds in integrative or alternative medicine.
Chelation Therapy FDA Approval
Q. Is chelation therapy FDA approved?
A. The FDA has approved chelation therapy for treating heavy metal poisoning, but its use for cardiovascular diseases and other conditions remains controversial and is not universally accepted.
Chelation Therapy For Autism
Q. Can chelation therapy be used for autism?
A. Chelation therapy has been explored as a treatment for autism, but its effectiveness and safety for this purpose are not well-supported by scientific evidence, and it is not widely recommended.
Chelation Therapy For CAD
Q. How is chelation therapy used for coronary artery disease (CAD)?
A. Chelation therapy for CAD involves using chelating agents to remove calcium deposits and improve blood flow in the coronary arteries. Its effectiveness is still under investigation./p>
Chelation Therapy For Heart Disease
Q. Can chelation therapy treat heart disease?
A. Chelation therapy may help treat heart disease by removing heavy metals and calcium deposits, potentially improving cardiovascular health. However, more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
Chelation Therapy For Heavy Metal Poisoning
Q. What is chelation therapy for heavy metal poisoning?
A. Chelation therapy for heavy metal poisoning involves using chelating agents to bind and remove heavy metals like lead, mercury, and arsenic from the body, reducing their toxic effects.
Chelation Therapy Near Me
Q. How can I find chelation therapy near me?
A. You can find chelation therapy clinics and certified therapists near you by searching online directories, consulting with your healthcare provider, or contacting professional organizations for recommendations.
Chelation Therapy Research
Q. What does chelation therapy research say?
A. Research on chelation therapy is ongoing, with studies exploring its effectiveness for various conditions, including cardiovascular disease and heavy metal poisoning. Results are mixed, and more research is needed.
Chelation Therapy Services
Q. What services are provided in chelation therapy?
A. Chelation therapy services include initial consultations, blood tests to determine heavy metal levels, administration of chelating agents, and follow-up care to monitor progress and ensure safety.
Chelation Therapy Side Effects
Q. What are the side effects of chelation therapy?
A. Side effects of chelation therapy can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, fatigue, low blood pressure, and kidney damage. It is important to have the therapy administered by a qualified professional.
Chelation Treatment
Q. What is involved in chelation treatment?
A. Chelation treatment involves the administration of chelating agents, usually through an IV, to bind and remove heavy metals from the bloodstream. Treatment plans vary based on individual needs and conditions.
Chelotherapy
Q. Is chelotherapy the same as chelation therapy?
A. Chelotherapy is another term used for chelation therapy, referring to the same process of using chelating agents to remove heavy metals and toxins from the body.
Cost of Chelation Therapy
Q. What is the cost of chelation therapy?
A. The cost of chelation therapy can vary widely depending on the provider, location, and number of sessions required. On average, it can range from $75 to $125 per session.
Detox Therapies
Q. What are detox therapies?
A. Detox therapies aim to remove toxins from the body and improve overall health. They can include chelation therapy, dietary changes, supplements, and other holistic approaches.
EDTA Chelation
Q. What is EDTA chelation?
A. EDTA chelation involves using the chelating agent EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) to bind and remove heavy metals from the bloodstream. It is commonly used for treating heavy metal poisoning and cardiovascular disease.
Environmental Medicine
Q. What is environmental medicine?
A. Environmental medicine focuses on the interactions between the environment and human health, studying how environmental factors contribute to
Functional Medicine
Q. What is functional medicine?
A. Functional medicine is a holistic approach to healthcare that focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of disease, often incorporating treatments like chelation therapy and personalized lifestyle changes.
Heavy Metal Detox
Q. What is heavy metal detox?
A. Heavy metal detox involves using various therapies, including chelation therapy, to remove heavy metals from the body and reduce their toxic effects on health.
Integrative Medicine
Q. What is integrative medicine?
A. Integrative medicine combines conventional medical treatments with alternative and complementary therapies, such as chelation therapy, to provide a holistic approach to patient care.
IV Chelation Therapy
Q. What is IV chelation therapy?
A. IV chelation therapy involves the intravenous administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals and toxins from the bloodstream, commonly used for treating heavy metal poisoning and cardiovascular conditions.
Lead Poisoning Treatment
Q. How is lead poisoning treated with chelation therapy?
A. Chelation therapy for lead poisoning involves administering chelating agents that bind to lead in the bloodstream, allowing it to be excreted from the body and reducing its toxic effects.
Metal Detoxification Therapy
Q. What is metal detoxification therapy?
A. Metal detoxification therapy uses chelating agents to bind and remove heavy metals from the body, helping to reduce their toxic effects and improve health.
Natural Detox Therapies
Q. What are natural detox therapies?
A. Natural detox therapies include dietary changes, herbal supplements, and lifestyle modifications designed to support the body’s natural detoxification processes and improve overall health.
Oral Chelation Therapy
Q. What is oral chelation therapy?
A. Oral chelation therapy involves taking chelating agents in pill or liquid form to remove heavy metals from the body. It is less invasive than IV therapy but may be less effective for certain conditions.